Ambimed-Group
Travel Medicine
Business Travel Medicine
Easily manage your reservations and stay constantly updated on Ambimed services.
|
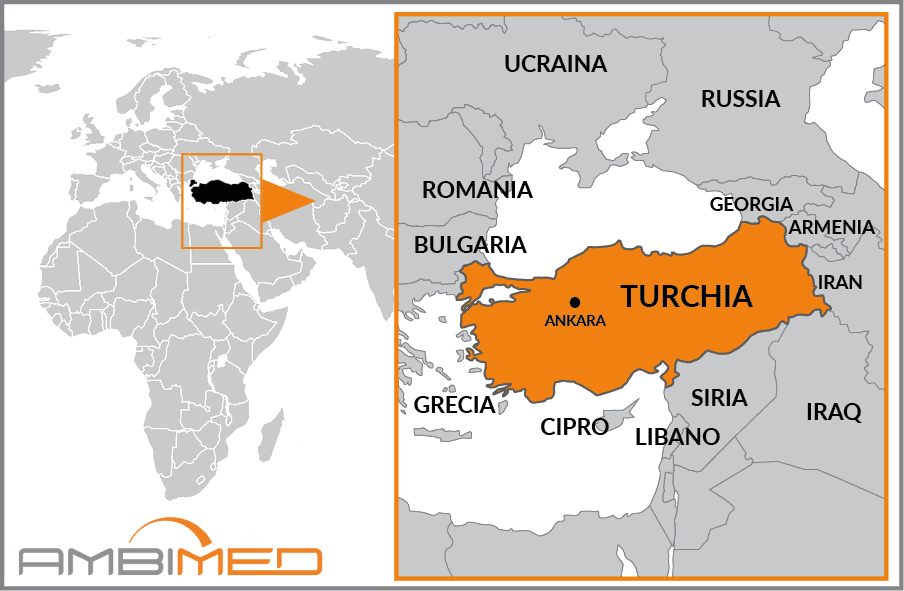
Country Name |
Republic of Turkey |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Surface area |
779,452 km² |
|
Capital |
Ankara |
|
Population |
77,695,904 (2014) |
|
Language |
Turkish |
|
Currency |
Turkish lira |
|
Time zone |
+1hr in relation to Italy |
|
Area code for Italy |
0039 |
|
Area code from Italy |
0090 |
Yellow fever vaccination is mandatory for all travelers over 1 year old from at-risk countries or who have transited for more than 12 hours at airports in at-risk countries.
Hepatitis A is generally transmitted through contaminated food and water, or through close physical contact with an infected person, while hepatitis B is transmitted through exposure to infected body fluids and blood.
Infection typically occurs through contact with the saliva of an infected animal, usually through bites, scratches or licks near open wounds or membranes (mouth, nose, eyes). The most common vectors are dogs and bats, but cases of infection in other domestic animals have also been reported.
Caused by toxins released by the bacterium Clostridium tetani, there is an endemic risk of contracting tetanus throughout the country.
Bacterial in origin, typhoid fever is transmitted through contaminated food and drink, especially in regions where sanitation conditions are poor.
Malaria, transmitted by mosquito bites, is widespread throughout the country. As a vaccine is not yet available, you are advised to take both behavioural and, following medical consultation, pharmacological preventive measures.
A disease of viral origin, it is transmitted by the bite of infected ticks. No cases have been reported in the country, but there is evidence to suggest the presence of potential risk. Vaccination is not considered necessary, but careful prevention measures are recommended.
Diseases such as Leishmaniasis and Japanese River Typhus are found in Southeast Asia. Transmitted by insect bites and with no vaccine, it is important to take preventive measures with behavioural prophylaxes.
The following vaccinations are strongly recommended as these diseases can be contracted anywhere in the world. Experts advise that you protect yourself and other travellers by making sure you are up-to-date with all of the recommended vaccinations. This will allow you to travel safely, while minimising the risk of exposure to infection.
Turkey is a state in Western Asia and to a small extent in Eastern Europe. Its territory is formed by two peninsulas: Thrace in Europe, the ultimate strip of the Balkan Peninsula, and Anatolia in Asia, separated from each other by the Dardanelles Strait. Its maritime borders are far more extensive than those of the land: in fact, the country is lapped by the Black Sea to the north, the Aegean Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean to the south. Its neighbouring states are Syria and Iraq to the south, Iran, Armenia and Georgia to the east, and Bulgaria and Greece to the northwest.
The coasts of Thrace are linear, with virtually no inlets. Slightly inland from the coastal areas there are elevations on three sides of the Anatolian Peninsula, with the highest peaks on the southern Taurus Range up to 3,500 m, which surrounded the Anatolian Plateau that is characterised by large wide basins on the southern strip.
Climatic conditions show great regional variability, with certain microclimates formed by hillside or coastal exposure. The coastal areas have a mild climate, but around the Black Sea areas the climate is colder than those of the Mediterranean. Inland areas have a continental climate, with a cold, snowy winter and hot, dry summer. Summer is dry and sunny throughout the country, and the driest months are July, August and September.