Ambimed-Group
Travel Medicine
Business Travel Medicine
Easily manage your reservations and stay constantly updated on Ambimed services.
|
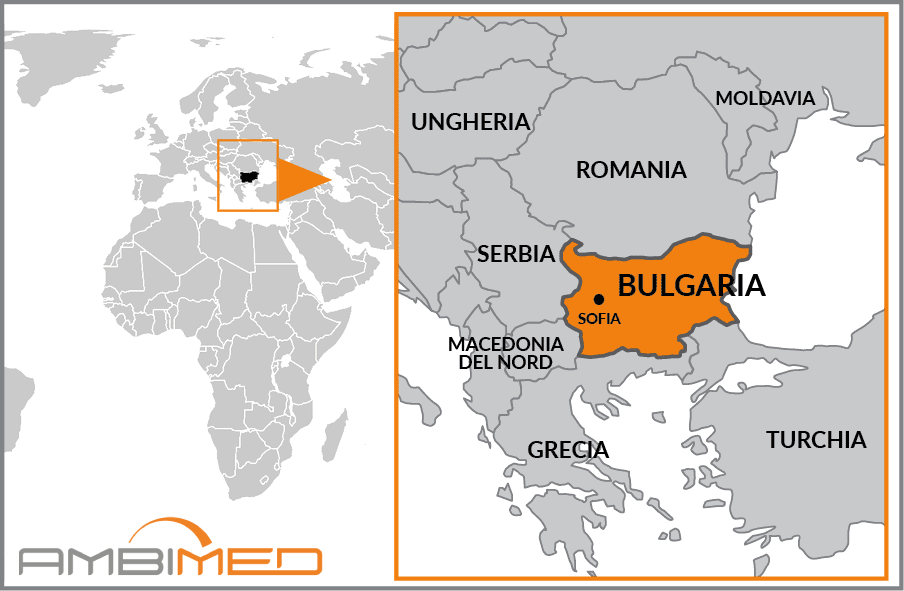
Country Name |
Republic of Bulgaria |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Surface area |
110,994 km2 |
|
Capital |
Sofia |
|
Population |
6,981,981 (2019) |
|
Language |
Bulgarian |
|
Currency |
Bulgarian Lev (BGN) |
|
Time zone |
+1hr compared to Italy |
|
Area code for Italy |
0039 |
|
Area code from Italy |
00359 |
Yellow fever vaccination is not required.
This viral disease is transmitted by the bite of infected ticks. Vaccination is recommended when staying in areas with a higher risk of infection. The risk decreases in the winter months.
Hepatitis A is usually transmitted by contaminated food and water, or close physical contact with an infected person, whereas Hepatitis B is transmitted by exposure to infected body fluids and blood.
Infection typically occurs through contact with the saliva of an infected animal, usually caused by bites, scratches or licks near open wounds or mucous membranes (e.g. mouth, nose, eyes). The most common vectors are dogs and bats, but cases of infection in other domestic animals have also been reported.
Caused by toxins released by the bacterium Clostridium tetani, the risk of tetanus infection is present throughout the country.
Diseases such as West Nile virus are present in Western Europe. As the disease is transmitted by insect bites and there is no vaccine, it is important to adopt careful behavioural and preventive measures.
The following vaccinations are strongly recommended as these diseases can be contracted anywhere in the world. Experts advise that you protect yourself and other travellers by making sure you are up-to-date with all of the recommended vaccinations. This will allow you to travel safely, while minimising the risk of exposure to infection.
Bulgaria is located in the north-eastern region of the Balkan Peninsula. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, which bathes its shores for just over 350km.
The main feature of the territory is the Balkan range, which from west to east divides the country into two halves, reaching a maximum height of 2,400 metres. The northern belt thins northward into the Danube lowlands, while toward the south the terrain features numerous river-crossed valleys.
The climate to the south of the Balkans is temperate-warm, while the north is continental. Generally speaking, the entire territory is little-affected by maritime influences. Annual temperatures are fairly steady, with quite a pronounced range over the Danube plain, which is more exposed to cold winds from the north, and where winter lows can exceed -20°C. Precipitation is more frequent in the highlands with snowfall in winter.