Ambimed-Group
Travel Medicine
Business Travel Medicine
Easily manage your reservations and stay constantly updated on Ambimed services.
|
Country Name |
Republic of Colombia |
|
Continent |
South America |
|
Surface area |
1,141,748 km² |
|
Capital |
Bogota |
|
Population |
47,121,089 |
|
Language |
Spanish |
|
Currency |
Colombian Peso (COP) |
|
Time zone |
-6hrs compared to Italy |
|
Area code for Italy |
0039 |
|
Area code from Italy |
0057 |
Yellow fever vaccination is mandatory for all travellers over 1 year of age arriving from Angola, Brazil, Democratic Republic of Congo and Uganda, or travellers who have spent more than 12 hours at an airport in these countries. Vaccination is recommended for travellers over 9 months of age heading to regions below an altitude of 2,300 metres. It is generally not advised (check with a doctor) for limited travel to the cities of Barranquilla, Cali, Cartagena, and Medellín. The vaccine is also not advised for travellers heading to areas above 2,300 meters, Bogota and the Caribbean department of San Andrés y Providencia.
Hepatitis A is usually transmitted by contaminated food and water, or close physical contact with an infected person, whereas Hepatitis B is transmitted by exposure to infected body fluids and blood.
Infection typically occurs through contact with the saliva of an infected animal, usually caused by bites, scratches or licks near open wounds or mucous membranes (e.g. mouth, nose, eyes). The most common carriers are dogs and bats, but cases of infection in other domestic animals have also been reported.
Caused by toxins released by the bacterium Clostridium tetani, the risk of tetanus infection is present throughout the country.
Bacterial in origin, typhoid fever is transmitted through contaminated food and drink, especially in regions with inadequate sanitary conditions.
Malaria is transmitted by the bites of infected mosquitos and is widespread throughout the country. As a vaccine is still not available, you must take careful precautions to avoid mosquito bites and in some cases it may be necessary to take antimalarial medication, after thorough evaluation by a qualified doctor.
These diseases are spread by the bites of infected mosquitos and there are currently no vaccines. Consequently, it is important to adopt careful behavioural and preventive measures.
Diseases such as Chikungunya, Leishmaniasis, American trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease) and West Nile virus are present in South America. As these diseases are transmitted by insect bites and there are no vaccines, it is important to adopt careful behavioural and preventive measures.
The following vaccinations are strongly recommended as these diseases can be contracted anywhere in the world. Experts advise that you protect yourself and other travellers by making sure you are up-to-date with all of the recommended vaccinations. This will allow you to travel safely, while minimising the risk of exposure to infection.
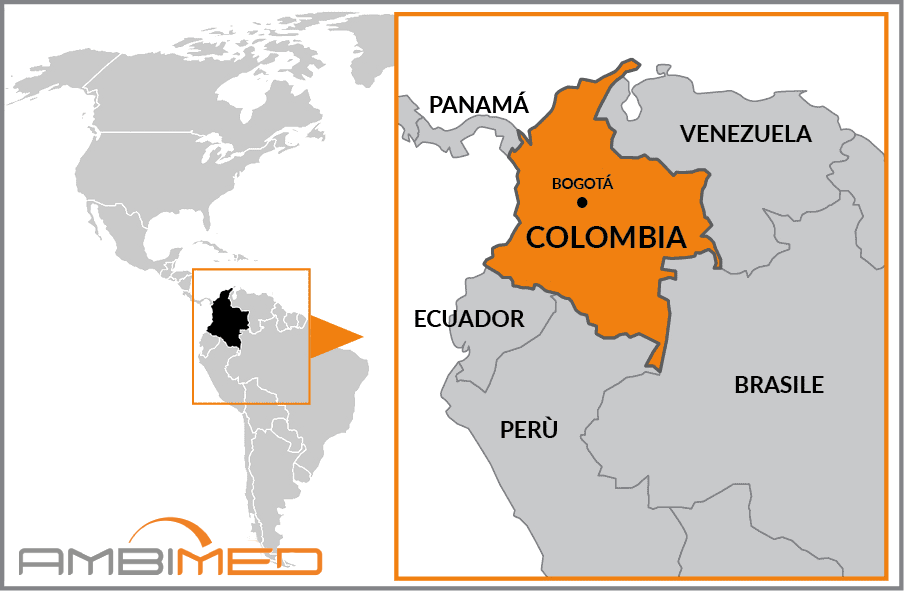
Colombia is a state in South America. The furthest north-western point borders Panama to the northwest, Ecuador to the southwest, Peru to the south, Brazil to the southeast, and Venezuela to the east and northeast. Two sides of the country overlook the sea: to the west the Pacific and to the north the Atlantic Ocean.
The country has two predominant geographical features that separate it into two distinct halves: the mountainous region in the west and the flat region in the east.
The reliefs are part of the northern Andean mountain range. They are divided into three parallel chains, separated from each other by a series of valleys, crossed by various watercourses. The Central Cordillera has numerous volcanoes (of the twenty-one recorded, five are at potential risk of eruption) and the highest elevation in the country, the 5,775 m Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta range in the north, which almost touches the Caribbean Sea. The coastline is generally flat and marshy, lined by forests on the Pacific side and savanna on the Caribbean side.
The mostly uninhabited eastern half of the country has extensive lowlands, developing into savanna in the north, while the dense Amazon rainforest grows luxuriantly in the south.
Colombia has a fairly diverse climate. The Pacific and Amazonian sides have an equatorial climate, the north-eastern side is characterised by savanna and subequatorial savanna, and the Andean region is strongly influenced by altitude. Rainfall is abundant on the Pacific side, where the country's highest rainfall levels are recorded, with less frequent rain on the Caribbean side.