Ambimed-Group
Travel Medicine
Business Travel Medicine
Easily manage your reservations and stay constantly updated on Ambimed services.
|
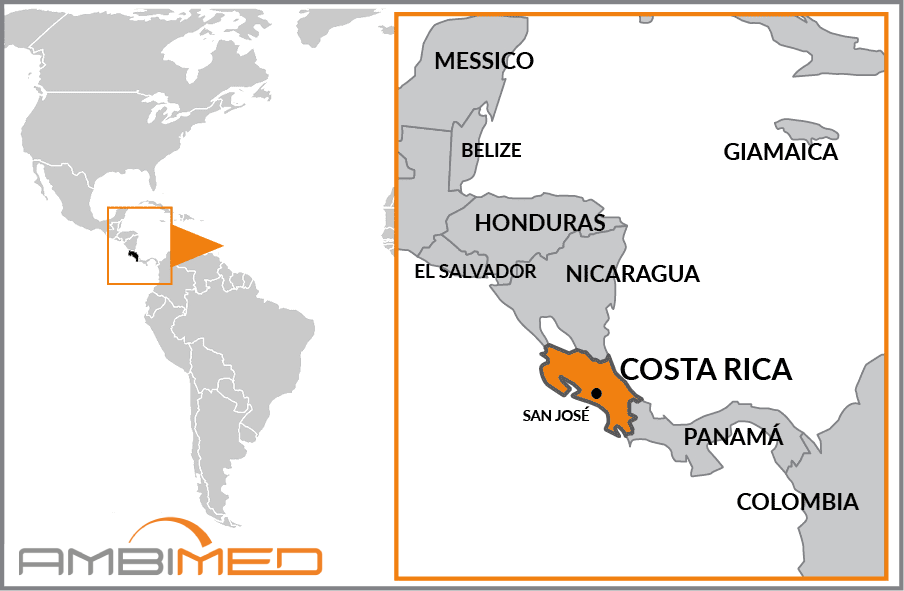
Country Name |
Republic of Costa Rica |
|
Continent |
Central America |
|
Surface area |
51,100 km2 |
|
Capital |
San José |
|
Population |
5,069,929 |
|
Language |
Spanish |
|
Currency |
Costa Rican Colón (CRC) |
|
Time zone |
-7hrs in relation to Italy |
|
Area code for Italy |
0039 |
|
Area code from Italy |
00506 |
Yellow fever vaccination is not required.
Hepatitis A is generally transmitted through contaminated food and water, or through close physical contact with an infected person, while hepatitis B is transmitted through exposure to infected body fluids and blood.
Infection typically occurs through contact with the saliva of an infected animal, usually through bites, scratches or licks near open wounds or membranes (mouth, nose, eyes). The most common vectors are dogs and bats, but cases of infection in other domestic animals have also been reported.
Caused by toxins released by the bacterium Clostridium tetani, there is an endemic risk of contracting tetanus throughout the country.
Bacterial in origin, typhoid fever is transmitted through contaminated food and drink, especially in regions where sanitation conditions are poor.
Malaria, transmitted by mosquito bites, is widespread throughout the country. As a vaccine is not yet available, you are advised to take both behavioural, and following medical consultation, pharmacological preventive measures.
These diseases are spread by mosquito bites and there is no vaccine. Therefore, it is important to take preventive measures by implementing behavioural prophylaxes.
Chikungunya and West Nile virus are to be found in certain areas of the Caribbean. Transmitted by insect bites and with no vaccine, it is important to take preventive measures with behavioural prophylaxes.
The following vaccinations are strongly recommended as these diseases can be contracted anywhere in the world. Experts advise that you protect yourself and other travellers by making sure you are up-to-date with all of the recommended vaccinations. This will allow you to travel safely, while minimising the risk of exposure to infection.
Costa Rica spans the Central American isthmus between the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Atlantic to the east. It borders Nicaragua to the north and Panama to the southeast.
The territory is almost exactly divided in a northwest/southeast direction by a central mountainous region. The elevations are mostly extinct or sporadically active volcanoes and on the southern belt reach a maximum peak of 3,800 m. As the altitude decreases, a series of central plateaus develop (at altitudes of 1,000/1,200 m above sea level), housing most of the population centres, unsurprisingly located where soil and climate conditions are most favourable.
The coasts are low and flat, those facing the Atlantic extend more widely with rainfall virtually all year round.
The climate is hot and humid, mitigated by the plateau altitude, where temperatures gradually drop on the peaks. Rainfall is abundant everywhere; concentrated on the Pacific side from June to November.